
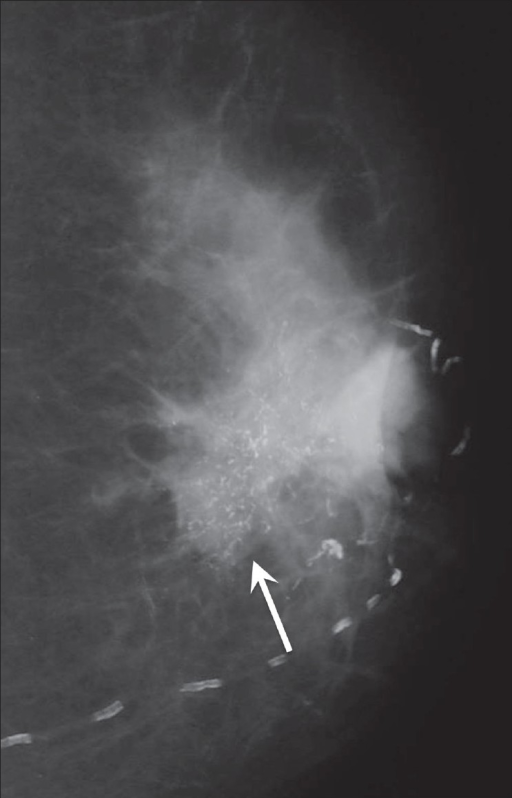
Worldwide, the most common invasive female cancer observed is breast cancer. The correlation between mammographic imaging features and breast cancer subtype was analyzed using Chi-square test, univariate and binary logistic regression analysis.Ĭonclusions: This study shows that BI-RADS 3–5 microcalcifications can be conveniently used to facilitate the preoperative prediction of HER2 and Luminal A molecular subtype in patients with infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Materials and Methods: Mammographic images of 485 female patients were included. other) and the patterns of mammographically detected calcifications. There was no significant difference between breast cancer subtypes (Luminal B vs. And we demonstrated that amorphour or coarse heterogenous calcifications were associated with a higher incidence of Luminal A subtype than pleomorphic or fine linear or branching calcifications. The model showed good discrimination for predicting Luminal A subtype, with a C-index of 0.74. In addition, multivariate analysis showed that calcification morphology (amorphour or coarse heterogenous calcifications OR: 2.847, 95% CI: 1.526 to 5.312) was independently predictive of Luminal A subtype. The model showed good discrimination for predicting HER2 subtype, with a C-index of 0.704. In univariate analysis, the clinicopathological parameters and BI-RADS 3–5 microcalcifications, which consisted 9 selected features was significantly associated with breast cancer molecular subtype (all P 2 cm in range (OR: 1.878, 95% CI: 1.150 to 3.067) and calcification > 0.5 mm in diameter (OR:2.206, 95% CI: 1.235 to 3.323) was independently predictive of HER2 subtype. Purpose: To investigate associations between breast cancer molecular subtype and the patterns of mammographically detected calcifications. Received: SeptemAccepted: JanuPublished: January 14, 2017 Zaiyi Liu, email: calcification, infiltrating ductal carcinoma, mammography, logistic regression, breast cancer molecular subtype
*These authors contributed equally to this work ChinaģDepartment of Radiology, Guangdong General Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province 510080, People's Republic of ChinaĤDepartment of Ultrasound, The Third People’s Hospital of Shenzhen, Guangdong Shenzhen 518112, China DongZhi Cen 1, *, Li Xu 2, *, Ningna Li 2, *, Zhiguang Chen 2, *, Lu Wang 2, *, Shuqin Zhou 2, *, Biao Xu 2, *, Chun ling Liu 3, Zaiyi Liu 3, Tingting Luo 4ġDepartment of Radiation Oncology and Department of Nuclear Medicine, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, 510150, Guangdong Province, People’s Republic of ChinaĢGuangdong Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province 510120, P.R.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
